|


|
Figure 1.1: | Microwave communication network.
|
|


|
Figure 1.2: | Gravitational forces between two masses.
|
|


|
Figure 1.3: | Gravitational field  1 induced by a mass m1. 1 induced by a mass m1.
|
|


|
Figure 1.4: | Electric forces on two positive point charges in free space.
|
|


|
Figure 1.5: | Electric field E due to charge q.
|
|


|
Figure 1.6: | Polarization of the atoms of a dielectric material by a
positive charge q.
|
|


|
Figure 1.7: | Pattern of magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
|
|


|
Figure 1.8: | The magnetic field induced by a steady
current flowing in the z-direction.
|
|


|
Figure 1.9: | A one-dimensional wave traveling on a string.
|
|


|
Figure 1.10: | Examples of two-dimensional and three-dimensional waves.
|
|


|
Figure 1.11: | Plots of y(x,t) = A cos( 2 t/T - 2 t/T - 2 x/ x/ )
as a function of (a) x at t=0 and (b) t at x=0. )
as a function of (a) x at t=0 and (b) t at x=0.
|
|


|
Figure 1.12: | Plots of y(x,t) = A cos( 2 t/T - 2 t/T - 2 x/ x/ )
as a function of x at (a) t=0, (b) t=T/4, and (c) t=T/2.
Note that the wave moves in the +x-direction with a velocity
up= )
as a function of x at (a) t=0, (b) t=T/4, and (c) t=T/2.
Note that the wave moves in the +x-direction with a velocity
up=  /T. /T.
|
|


|
Figure 1.13: | Plots of y(0,t) = A cos [(2 t/T) + t/T) + 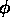 0] for three
different values of the reference phase 0] for three
different values of the reference phase 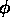 0. 0.
|
|


|
Figure 1.14: | Plot of y(x) = 10e-0.2xcos( x)
meters. Note that the envelope is bounded between the curve given by
10e-0.2x and its mirror image. x)
meters. Note that the envelope is bounded between the curve given by
10e-0.2x and its mirror image.
|
|


|
Figure 1.15: | The electromagnetic spectrum.
|
|


|
Figure 1.16: | Individual bands of the radio spectrum and their primary
applications.
|
|


|
Figure 1.17: | Relation between rectangular and
polar representations of a complex number z = x + jy = |z|ej . .
|
|


|
Figure 1.18: | Complex numbers V and I in the complex plane (Example
1-3).
|
|


|
Figure 1.19: | RC circuit connected to a voltage source vs(t).
|
|


|
Figure 1.20: | RL circuit (Example 1-4).
|
|


|
Figure 1.21: | Wave on a string tied to a wall at x=0 (Problem 1.6).
|